Iterator Task
The iterator task will go through an input list or dictionary and will trigger tasks connected to the yellow port.
Each iteration will provide the following variables:
loop_indexloop_key(dictionary only)loop_valueloop_sizeend_of_loop(True/False)
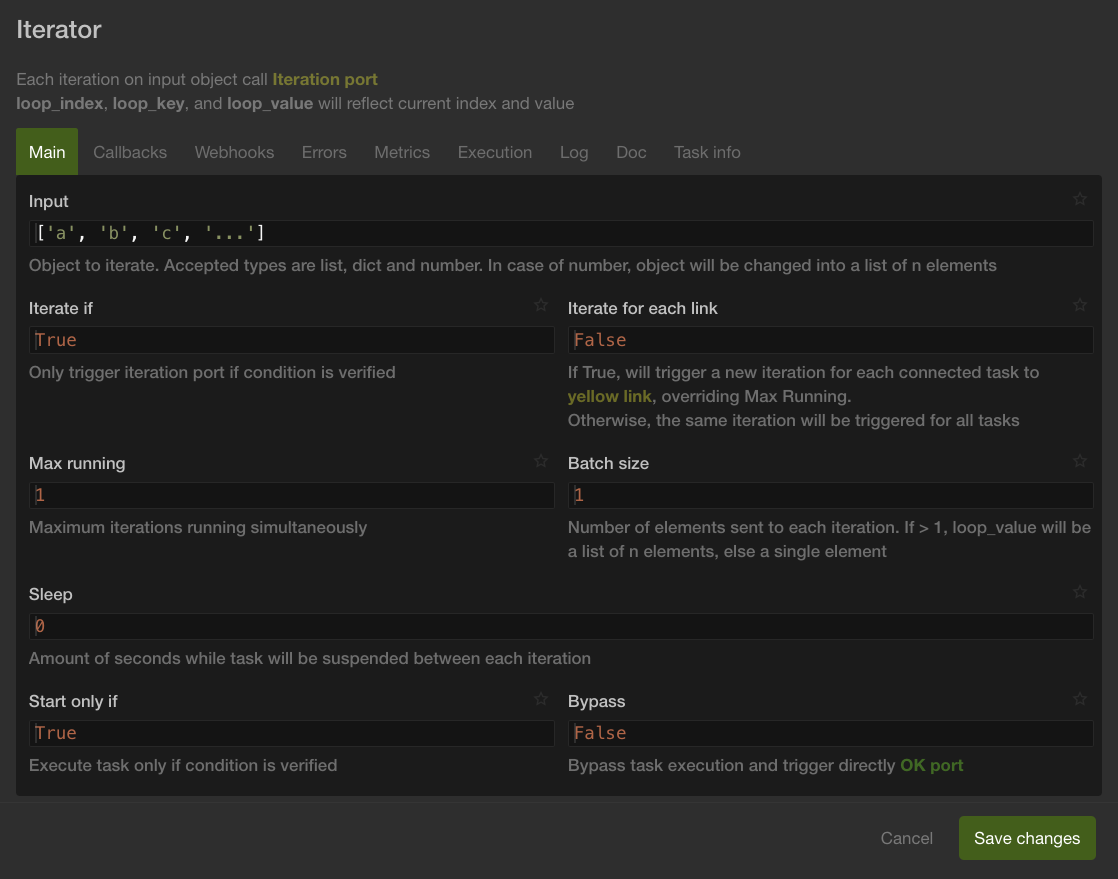
Input
Python list or dictionary. If a string is provided, it will be decoded as a json component.
Iterate if
Triggers the yellow port only if condition is verified. This parameter is evaluated before each iteration, and loop_index is incremented even if iteration is not triggered.
Pseudocode equivalent
For_each value in INPUT
If ITERATE_IF is True
Execute Yellow port
Else
Next value
loop_index = loop_index + 1
Max running
Defines the maximum concurrent iterations. If greater than 1, iterator will trigger a batch of n iterations and wait for termination of the first one before triggering another one. Note that an iteration could be composed of various links, like the following example.
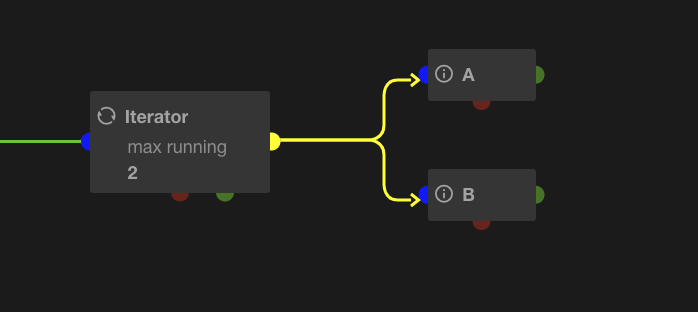
In this case, 2 iterations will be triggered at the same time:
Iteration loop_index 0:
- trigger task A
- trigger task B
Iteration loop_index 1:
- trigger task A
- trigger task B
Once an iteration is terminated (i.e tasks A and B are ended), the next one is triggered to reach max running iterations.
NB: there is no guaranty about the tasks order when iterations are triggered (task A could be started after task B).
Iterate for each link
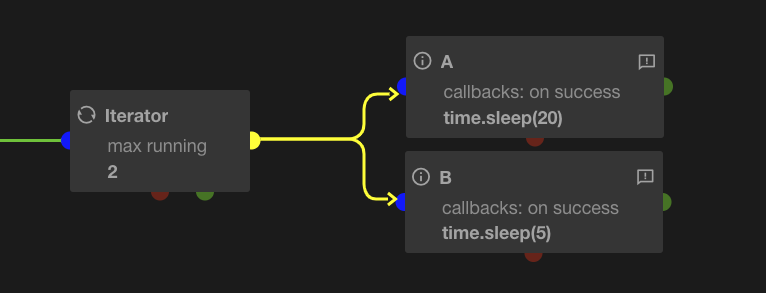
Instead of triggering all linked tasks for 1 iteration, this parameter will trigger 1 iteration by linked task. Each task will receive a unique loop_index, and a new iteration will be triggered as soon as a previous one is terminated.
The previous example will generate the following output.
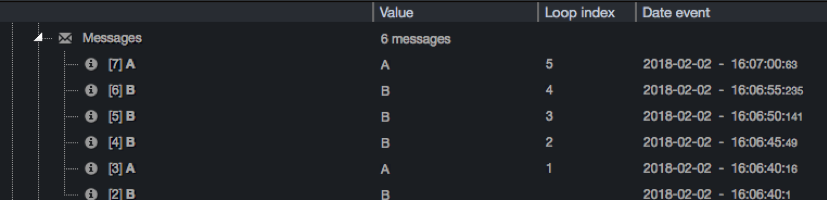
-
Tasks A and B are first started, with respectively 1 and 0 as loop_index (note that task B started before task A, independently of the graph representation).
-
While A is sleeping for 20 seconds, B will be executed 3 more times, as it's sleeping only for 5 seconds. Each of started tasks B will have a different "loop_index".
-
And so on, depending on each task duration...
Batch size
If greater than 1, each loop_value will be a subset of n input elements.
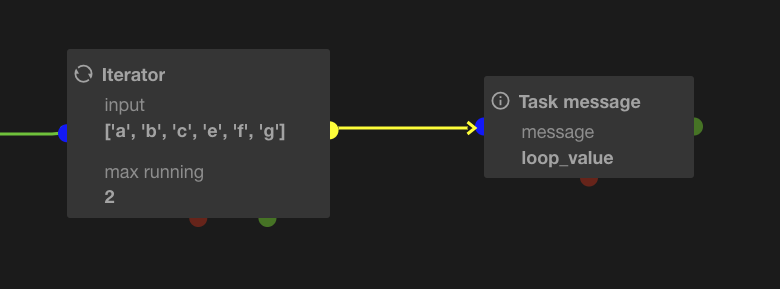
This example will produce 4 iterations with the following loop_value.
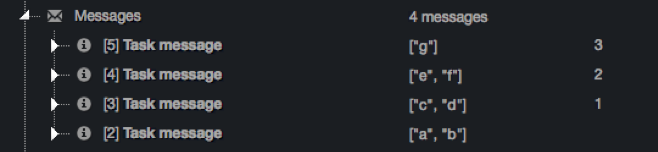
Note:
- loop_index is relative to the subset, and not to the global input.
- The final subset could have less than batch size elements.
Sleep
Defines the amount of execution sleep time between each iteration.